There are both advantages and disadvantages of polymer membranes. The alternative to polymer membranes is ceramic membranes. Ceramic membranes are a more expensive alternative. Yet, there are significant differences between the membrane properties.
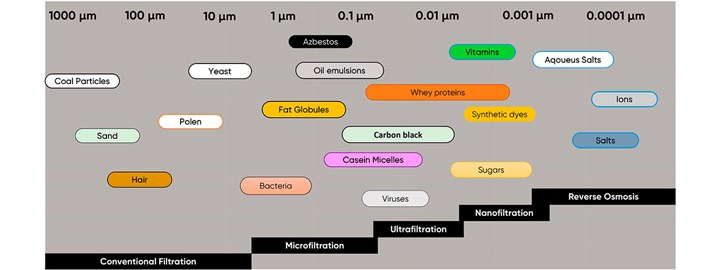
Organic membranes are used in many industries. The main advantage of organic membranes is the low capital expenditure due to low manufacturing costs and easy scalability. Therefore, these membranes have been used for many industrial water treatment applications. Polymer membrane technology is especially suitable for water desalination processes through reverse osmosis. The polymeric material cellulose acetate is often employed for water treatment due to its high chlorine tolerance.
However, due to the polymeric membrane properties, the balance flips towards ceramic membranes within several industries and water treatment applications.
Polymer membranes suffer from a low degree of mechanical, thermal, and chemical stability. Contrary, ceramic membranes possess a high degree of these exact attributes. This makes polymer membrane technology an inadequate technology for harsh industries, ultimately calling for ceramic membranes with stronger properties.
Ceramic membranes have the advantage of being able to withstand harsh chemical cleaning, high temperatures, and aggressive fluids with acids or strong solvents. Thus, ceramic membranes can be used in harsh environments, such as corrosive and high-temperature environments, where polymer membranes are inadequate. These industries can be:
- Power plants
- Oil and gas
- Marine
- Mining
With the current focus on sustainability and the rapid implementation of environmental regulations and discharge limits for various industries to obtain cleaner industrial processes, it becomes more and more essential to have durable and cost-effective filtration solutions that can withstand arduous industries.
Moreover, ceramic membranes can withstand harsh chemical cleaning for sterilization and frequent backwash, which is crucial for several industries in order to maintain superior hygiene standards. Any compromises on cleaning and sterilization can contaminate the operation and result in operational downtime. Industries with extensive hygiene needs can be:
- Pharmaceutical
- Cosmetics
- Biotech
- Food and beverage
- Dairy
As ceramic membranes are more expensive to produce, they are linked with higher capital expenditure. Yet, this is compensated by an efficient membrane with a long lifetime, ensuring a low cost of ownership. The durable and hard inorganic material delivers a robust and stable membrane, which provides efficient and reliable operation and can withstand strong pressure and the stress it causes. As organic membranes are not as durable, they have a shorter lifetime and generally require more frequent replacement.