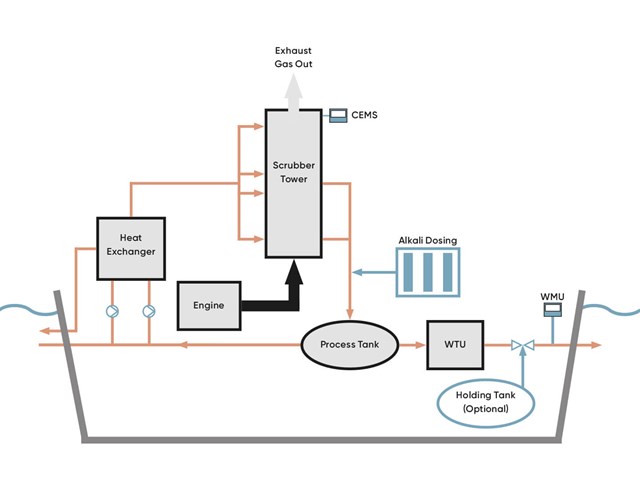
A closed-loop scrubber is an exhaust gas cleaning system (EGCS) that controls air pollution on a vessel. This method is crucial to comply with the strict IMO 2020 sulfur cap as it reduces sulfur oxides (SOx) emissions from marine exhaust gas streams by 98%. However, a closed-loop scrubber consists of various elements and complex processes. Let us be more detailed about how a closed-loop scrubber works.
When operating the ship’s engine, the auxiliary engine or boiler generates exhaust caused by combustion processes. Before the shipping industry focused on desulfurization, the exhaust gas went directly into the atmosphere, which caused acid rain, harming people, wildlife, and the planet. Today, the exhaust gas can be cleaned with an exhaust gas cleaning system employing unique scrubber technology, delivering 98% removal of sulfur. This ensures a more sustainable operation and essentially compliance with the IMO 2020 sulfur cap by lowering SOx emissions. The scrubbers reduce SOx emissions from 3.5% to less than 0.1%, allowing ships to operate within the ECA.
There are three types of scrubbers; open-loop, closed-loop, and hybrid. Read more about them and how they differ here.