What is ultrafiltration?
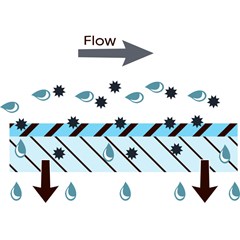
UF is a pressure-driven membrane filtration technique used to treat various types of water and wastewater to remove suspended solids and solutes.
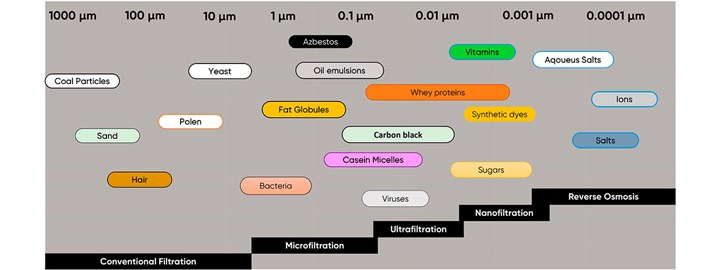
There are four filtration ranges within membrane filtration. These enable targeted particles to be removed and targeted particles to be withheld in liquid. The filtration ranges are microfiltration, ultrafiltration, nanofiltration, and reverse osmosis. It is the membrane selectivity, also called the rejection rate, that sets the filtration ranges apart. UF separates suspended solids and solutes of high molecular weight within the range of 0.01 to 0.1 microns. One micron is equal to one-millionth of a meter. UF can, among others, be used to remove bacteria, viruses, colloids, proteins, pyrogens, and pathogens. The technology is used in multiple industries to treat various kinds of water and wastewater.